Woodpeckers are fantastic birds, sought after for pecking wood and playing their part in woodlands. But here is something interesting: the males and females typically vary both in looks and behavior. Although such variations, sometimes subtle, have a big role in determining what makes them tick as well as with the manner in which they play with nature.
In this article, the major differences between the male and female woodpeckers are discussed, with a full guide for bird watchers of every standard, in addition to useful pictures of male and female woodpeckers for identification purposes.
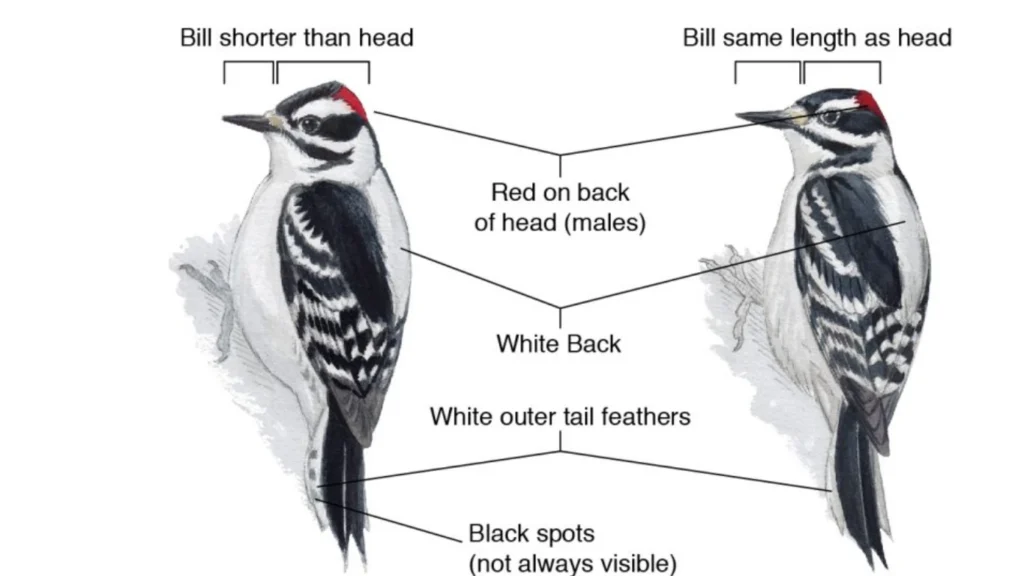
Identifying Woodpecker Sex: Plumage Clues

One of the most stark differences between the male and female woodpeckers is the plumage, or body feathers. Some are extremely showy, but others make one need to notice a little more. This is particularly true when side by side, a lesser spotted woodpecker male is compared to that of the female.
The Classic Red Patch: A Male Trademark
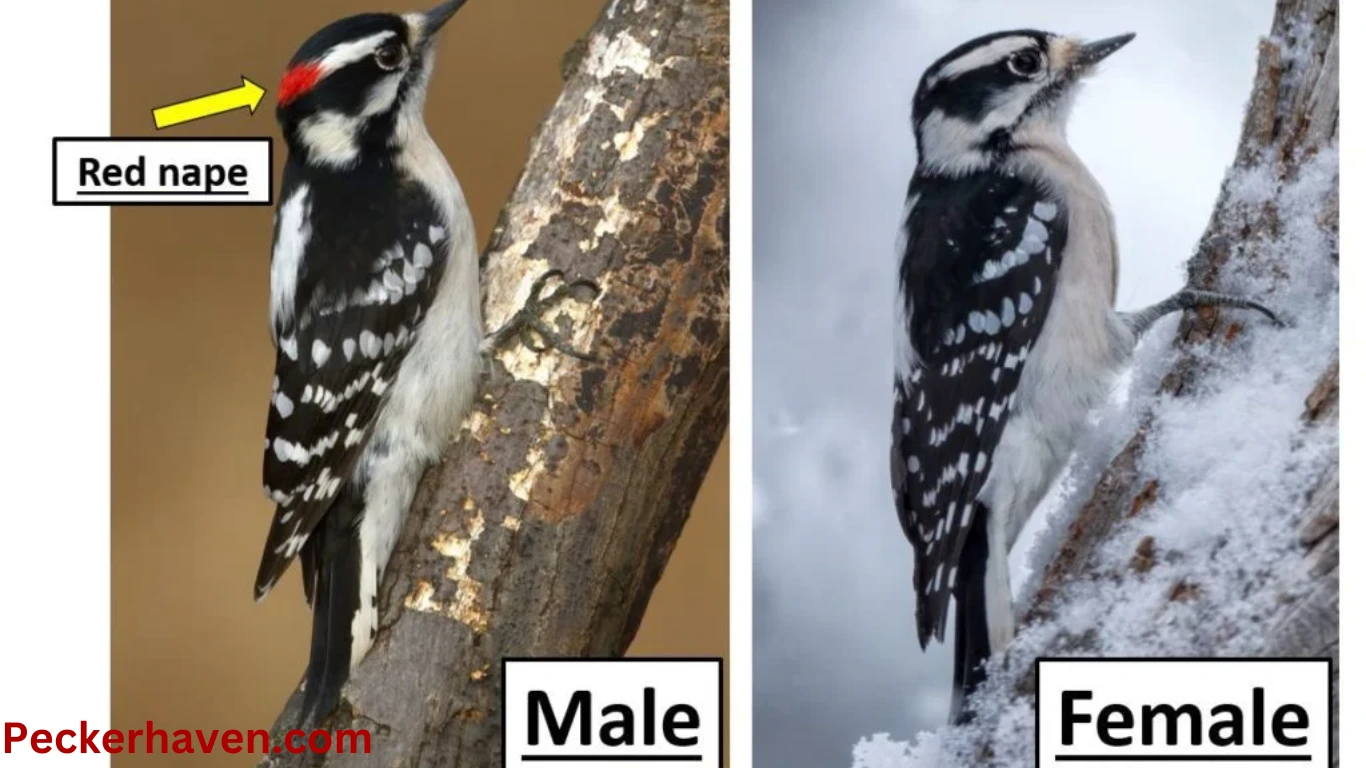
A few of the woodpeckers, such as Downy Woodpecker, Hairy Woodpecker, and Red-bellied Woodpecker, will also bear a red spot on the head. The red spot is a sure indicator of a male.
The females of both of these species also typically don’t have this bright mark, instead more subdued color to the head in black, white, and brown, usually some combination of all three. Attempting to be able to imagine it correctly, checking online to find downy woodpecker male female photos may help.
Subtle Color Variations: Beyond the Red
Even in those animals where the males and females do have some red, there can be variations. Both the male and female of the Red-headed Woodpecker, for example, have red heads, but red on a male head extends down to the neck and to the breast. Only on the female’s head is the red restricted. It is also very large in seeing a female pileated woodpecker compared to males.
Wing and Back Patterns: Another Clue
While head markings are the most obvious difference, paying attention to wing and back patterns can also help. Some species might show slight variations in the barring or spotting patterns on their wings and backs, though these are often more challenging to spot and require a good field guide or binoculars. These subtle differences are important to note when trying to identify a female spotted woodpecker.
Behavioral Differences

Beyond their physical appearance, male and female woodpeckers also exhibit differences in their behavior.
Drumming: A Male’s Loud Declaration
Drumming, or tapping rapidly on trees, is typical of woodpeckers, but drumming is done by the males primarily for communication. The males drum to signal territorial markers, summon a mate, and announce themselves to competitors. Although females may drum at times, the drumming is done enthusiastically by the males.
Nesting Duties: A Shared Responsibility, But with a Twist
Male and female woodpeckers help in nest activities, though there is a thin line when it comes to their roles. The males prepare the nest cavity, while females concentrate on internal preparation and lining. Both the parents take shifts in incubating, but the male would prefer night duty.
Feeding the Young: Teamwork Makes the Dream Work
After the eggs hatch, parents both work hard to feed nestlings. However, males are able to bring food to the nest more often than females, particularly in the initial period of chick life. Even a young pileated woodpecker profits from this cooperative system.
Size Differences: A Matter of Inches
In most woodpecker species, there is little to no significant size difference between males and females. They are generally the same size.
The Exception to the Rule: Larger Females
In a few species, like the Pileated Woodpecker, females might be slightly larger than males. However, this difference is usually subtle and not easily noticeable in the field.
Overlapping Measurements: Size Isn’t Always Reliable
Even when there are slight size differences, the ranges of measurements for males and females often overlap. This means that size alone isn’t always a reliable way to distinguish between the sexes.
Vocalizations: More Than Just Drumming
Woodpeckers are known for their drumming, but they also produce a variety of vocalizations.
Calls and Songs: Subtle Sex-Specific Variations
Although both sexes employ calls and song, there may be slight difference in the kind of call they produce or how often they call. These differences are usually very small and need a sharp ear to pick up. Knowledge of female woodpecker calls is useful for identification.
The “Wik-wik” Call: A Common Woodpecker Sound
One common woodpecker call is a sharp “wik-wik” sound. Both males and females use this call, but the context and frequency might vary.
Summary of Differences Between Male and Female Woodpeckers
| Feature | Male Woodpecker | Female Woodpecker |
|---|---|---|
| Plumage | Often has a red patch on the head | Typically lacks a red patch on the head |
| Drumming | Frequently drums to establish territory | Drums less frequently than males |
| Nesting Duties | Excavates the nest cavity, incubates at night | Prepares the nest interior, shares incubation |
| Feeding Young | Brings food to the nest, often more frequently | Shares feeding duties |
| Size | Generally the same size or slightly smaller | Generally the same size or slightly larger |
| Vocalizations | May have subtle variations in calls | May have subtle variations in calls |
Examples of Woodpecker Species and Their Differences
| Species | Male Characteristics | Female Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Downy Woodpecker | Red patch on the nape | Black and white pattern on the head |
| Hairy Woodpecker | Red patch on the back of the head | Black and white pattern on the head |
| Pileated Woodpecker | Red crest, slightly larger | Red crest, slightly smaller |
| Northern Flicker | Black “mustache” stripes, red crescent on nape | Lacks black “mustache” stripes |
Conclusion
While some of the differences between woodpeckers of the male and female types are clear, others require keen observation. Watching elements of plumage, habits, and calls and relying on material like female woodpecker pictures, bird enthusiasts will appreciate the intriguing bird species more.
Respecting these differences not only adds an extra flavor to bird watching but also transfers immensely into woodpecker habits and ecological research.
FAQs
How do I just tell if it is a male Downy Woodpecker?
The easiest way to know whether it is a male Downy Woodpecker is to look for the red spot at the rear of its head. Males do not have this red spot. Downy woodpecker male vs female photo may be useful.
Do females drum at all?
While drumming is a male behavior, females will drum every now and then, especially when defending territory or communicating with their mates.
Are males and females any woodpeckers totally unrecognizable by appearance?
There are certain woodpeckers whose males and females are distinguishable from one another in the slightest manner and at times even require close examination. But there generally is at least some subtle hints, though not necessarily contemporaneous. This could make it difficult to differentiate lesser spotted woodpecker male and female.
Why do male woodpeckers possess a red spot on their heads?
The red head spot of a male woodpecker is believed to be employed in mate choice and competitor signaling. It’s a signal that enables them to close their territory and gain a mate.
What is the function that drumming serves in woodpecker communication?
Drumming serves a variety of purposes in woodpecker communication. Male drumming is utilized for marking territories, to call females in, and to warn potential competitors that they are present. It is an open system of communication within the forest environment.
